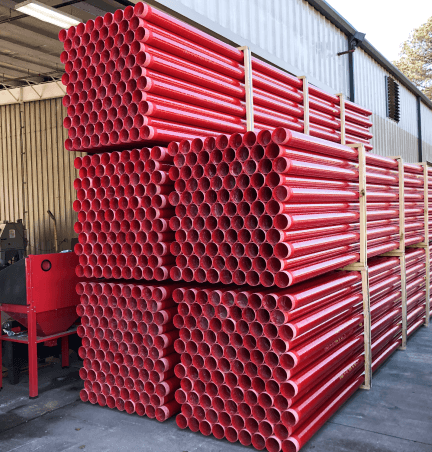
- Corrosion can be caused by chemical reactions such as oxidation and includes galvanic corrosion, atmospheric corrosion, and uniform corrosion
- Environments where corrosion occurs include wastewater treatment plants, chemical plants and coastal environments such as piers and ports
- In industrial construction project applications in corrosion-prone environments, it’s important to select a corrosion-resistant conduit for longevity and better return on investment
What is corrosion resistance?
Corrosion resistance is the ability of a substance or substrate to resist deterioration and damage caused by chemical or electrochemical reactions or oxidization.
The most common types of corrosion include:
- Uniform corrosion
- Pitting corrosion
- Crevice corrosion
- Galvanic corrosion
- Stress corrosion cracking
- Inter-granular corrosion
- High-temperature corrosion
- Atmospheric corrosion
- Microbial corrosion
Resistance to these factors varies and can be a result of the material’s inherent properties, or a result of additional protective measures such as paints, tape and shrink wraps, or PVC-coating.
Prevent this from happening in your wastewater or chemical plant project with corrosion-resistant electrical conduit.
How do environmental factors affect corrosion resistance?
Natural environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, as well as industrial elements like dust and exposure to harsh chemicals can affect the ability of both metallic and nonmetallic electrical systems to combat corrosion to varying degrees.
Industrial settings are especially susceptible to corrosion, and few environments are more caustic than wastewater treatment facilities where sodium hypochlorite (bleach), polymer wastewater sludge, liquid oxygen, and waste-activated sludge can wreak havoc on aging electrical conduit systems. Chemical plants, refineries, food and beverage process plants, and mining environments all pose similar threats.
Marine and coastal environments, as well as bridge and transportation settings, can also introduce highly corrosive elements like salt from saline ocean and bay water as well as road maintenance efforts to electrical systems.
Why is corrosion resistance important when choosing electrical conduit?
Left unchecked corrosion can cause millions of dollars of damage related to repairs and replacements, and in some cases, life-threatening conditions including explosions in refineries and gas transmission plants. Corrosion may be inevitable, but it is controllable. By specifying a highly corrosion-resistant electrical conduit type engineers can expand the lifespan of an electrical system, reducing costs for time, materials, and labor over time, and improve environmental safety for countless workers.
Traditionally PVC conduit has been used in electrical raceway systems requiring corrosion resistance in low to moderate temperate environments (PVC conduit is not rated for high temperatures), however, shortages of PVC base resins have been limiting the availability of these materials since 2020.
Aluminum conduit is rated for solvents like acetone as well as fuels, but is not recommended for salts, alkaline materials, mild acids, or oxidizing agents due to its limited corrosion protection.
RMC (rigid metal conduit) or rigid steel conduit is susceptible to corrosion in harsh environments, threatening the integrity and durability of the electrical system without the addition of PVC coating or the application of zinc coating through hot-dip galvanizing.
Fiberglass conduit, or RTRC electrical conduit pipe, offers the broadest range of corrosion resistance among in-market electrical conduit materials. RTRC is corrosion-resistant to many chemicals and an appropriate choice for highly corrosive environments like wastewater treatment and chemical plants, bridges, and coastal applications.
Applicable Standards
The National Electrical Code (NEC®) establishes guidelines for material use by Class, Division, and Group. It is important to check the NEC rating of conduit products by manufacturer, as their product standards may fall above or below the substrate guidelines provided by the NEC. Refer to NEC Article 501 (Gasses, Vapors, and Liquids), Article 502 (Dusts) and Article 503 (Fibers and Flyings) for more details.
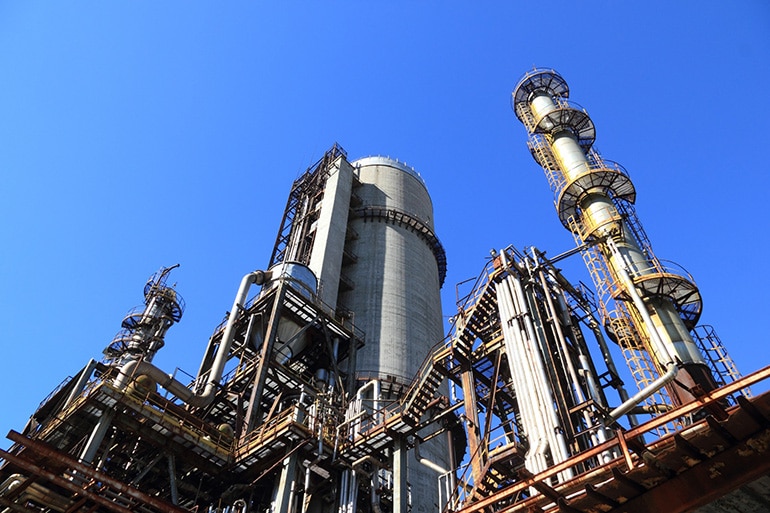

Chemical plants are harsh environments that require corrosion-resistant electrical conduit to protect conductors.
Learn how fiberglass conduit contributed to success in a wastewater treatment facility and see how our fiberglass reinforced epoxy conduit performs in chemical plants. For specific questions about custom conduit and situations, contact us.
Keep Reading
Champion Fiberglass® Named a CompositesWorld Top Shop for 2024
The origins of fiberglass date back to the ancient Greeks. Today fiberglass is used for a variety of applications from…
Get to Know Research and Development Engineer Blake Rogers
He’s got a diverse background in engineering, is new to Texas and can juggle. Meet Blake Rogers.
Electrical Conduit Cost Savings: A Must-Have Guide for Engineers & Contractors
To help identify cost savings that don’t cut corners on quality, Champion Fiberglass developed a free resource for engineers and…