The electroindustry is increasingly recognizing the benefits of using lightweight-yet-strong fiberglass conduit (RTRC) in place of heavier, costlier electrical conduit materials like PVC-coated steel and GRC. Champion Fiberglass offers concrete information around the benefits, both material and financial, that set this product apart.
These resources are a good starting place to begin comparing fiberglass conduit to other commonly used in-market industrial conduit materials. Make a more informed choice with:
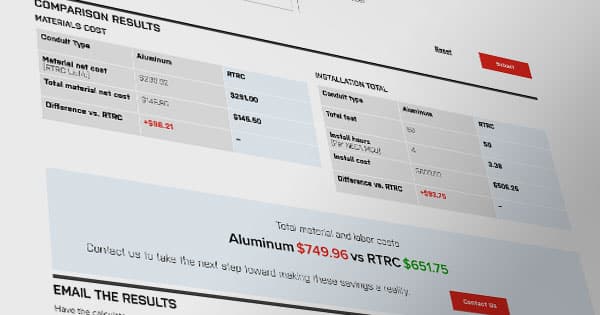
The Conduit Calculator
Enter your project specifics and compare cumulative installation and material costs for fiberglass (RTRC) vs. PVC-coated steel, GRC, aluminum, and stainless steel electrical conduits.

Fiberglass Conduit FAQs Resource
From manufacturing to applications and usage, our FAQs bring together the answers you need to make product and installation decisions.
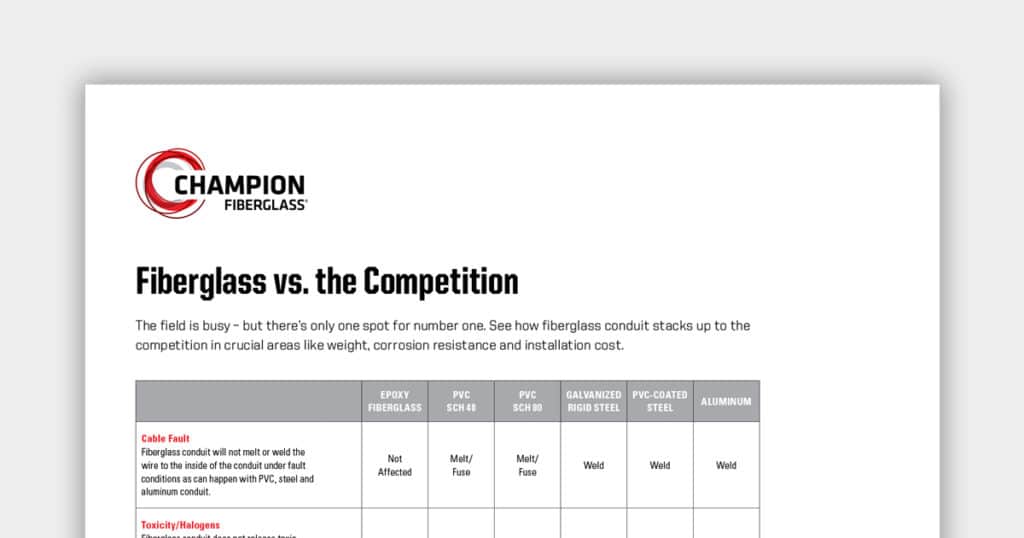
Fiberglass vs. the Competition Comparison chart
Our comparison chart shows relative weights, toxicity, UL Listed support span distances, and more. Compare Champion Fiberglass to other electrical conduit materials at a glance.
Champion Fiberglass. Do More. Spend Less.
Lightweight wins.
4″ diameter SW Champion Fiberglass conduit weighs in at 13.7x lighter than PVC-coated steel and GRC.
Lighter electrical conduit means lower installation costs and better savings.
Easy installation = savings.
Install a 100′ length of both 6″-diameter Champion Fiberglass Duct® and PVC-coated steel. According to the NECA Manual of Labor Units:
9 hours
60 hours
The difference is clear. So are the savings.
Leading the fight against corrosion.
Champion Fiberglass products offer leading corrosion resistance, making them the right choice for a number of caustic environments and challenging cabling applications.
These are just a few of the benefits of choosing Champion Fiberglass conduit over the competition. Learn why Champion Fiberglass is superior.
Leading-edge Facility and Manufacturing Processes
Champion Fiberglass is committed to delivering products that conform to the highest manufacturing standards. To that effect, we constantly strive to ensure that our facility and manufacturing practices are innovative and up-to-date, contributing to the overall cost efficiency of our products.
See a full list of our industry alliances and product and facility standards here.
Selecting an Electrical Conduit Type
The right electrical conduit type for your project will depend on the application, type of installation (above ground or below ground), building codes, and environmental factors like corrosion, UV exposure, weather and safety concerns such as fire. Electrical conduit is available in metallic and non-metallic materials, in flexible or rigid styles. Some of the more common rigid electrical conduit substrates used in industrial construction include:
Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC)
- This conduit is made from steel and provides impact resistance. It is used in industrial and commercial applications. It’s a long-time industry standard but very heavy and highly susceptible to corrosion.
Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing (ENT)
- ENT includes PVC conduit and is subject to “burn-through.” It is currently experiencing high prices and delivery delays due to a worldwide shortage.
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT)
- EMT conduit is made of aluminum or steel typically with thinner walls and lighter than GRC. It is often used in residential projects.
Fiberglass Conduit (RTRC)
- This electrical conduit is lightweight and durable, cost-competitive, and readily available. It is approved for use across many applications including data centers, utilities, and wastewater treatment.
Your Questions. Champion Fiberglass Answers.
Visit our FAQ resource to learn more about ease of installation, how fiberglass industrial conduit (RTRC) helps build savings, manufacturing, product specifics, and more.